Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism
Products 214 to 215. As shown in the following figure a hydrogen ion catalyzes the Markovnikovs addition.
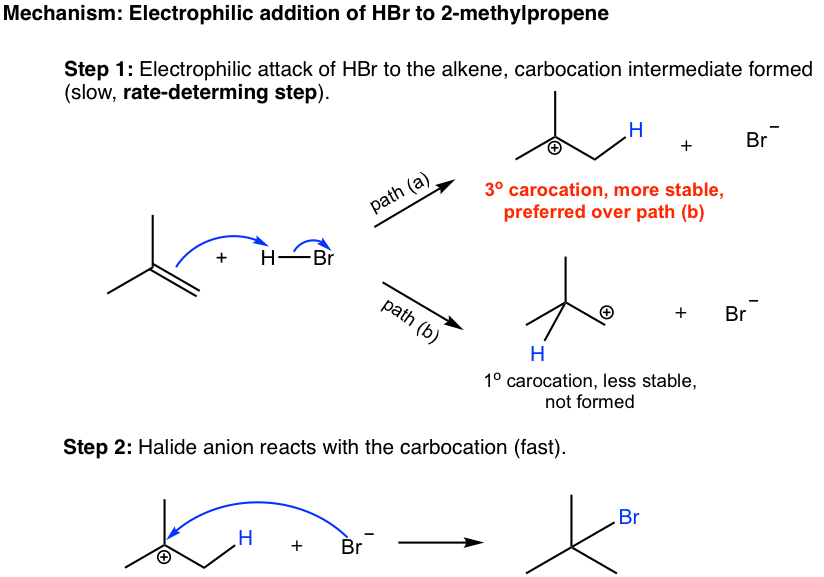
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
Mechanism The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps.

. Such an encirclement arrangement and open stereochemical framework endow the single Pd atom with the power to activate hydrogen H 2 thereby enabling the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes under mild conditions. Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes with Practice Problems. Carbon and hydrogen while in the ketones it is bonded to two carbon atoms.
Similarly groups that favor ionization of the halogen may generate a transition state with substantial positive charge on the alpha-carbon and only a small degree of CH breaking. The NHC ligands on the cluster as revealed by density functional theory DFT calculations are key factors in determining the selectivity of the. Electrophilic addition to conjugated dienes occurs through 12 and 14-addition mechanism out of Q.
Drawing formulas from names. For example if the Rgroups on the beta-carbon enhance the acidity of that hydrogen then substantial breaking of CH may occur before the other bonds begin to be affected. Notably for products 210 and 214 12 to 14 racemization is observed which can be explained by the comparably high acidity of the α-hydrogen atom in the case of the starting 2.
Matching alcohols to their names I. Drawing alcohol formulas. S N 1 S N 2 E1 or E2 the Largest Collection of Practice Problems.
The ability of hydrocarbons to bond to themselves is known as catenation. Reaction Mechanism Click Here for Sample Questions The haloalkanes or aryl halides with sp 3 or sp 2 hybridised carbon atoms when reacted with Magnesium metal give Grignard reagent which is an organometallic compound. Drawing formulas from names.
Addition Reactions of Alkenes. The carbonyl compounds in which carbon of carbonyl group is bonded to carbon or hydrogen and oxygen of hydroxyl moiety -OH are known as carboxylic acids while in compounds where carbon is attached to carbon or hydrogen and nitrogen of -NH2 moiety or to halogens are called amides. With such capabilities they can.
Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols. CH 3 CHCH 2 HI CH 3 CHICH 2 H. Delydrobalogenation of vinyi halides is essentially.
The primary alcohols elimination reactions follow the E2 mechanism whereas the secondary and tertiary alcohols. Hydrohalogenation is the addition of hydrogen halides such as HCl or HI to alkenes to yield the corresponding haloalkanes. Only one textbook in this admittedly incomplete sample mentions the S N i mechanism at all.
S N 1 S N 2 E1 E2 How to Choose the Mechanism. The antiMarkovnikovs addition results from a hydroborationoxidation reaction. If its not in the textbook chances are it.
Formation of alkenes. This is mainly due to the self-bonding or catenation of carbon that prevents the complete saturation of the hydrocarbon by the formation of double or triple bonds. If the two carbon atoms at the double bond are linked to a different number of hydrogen atoms the halogen is found preferentially at the carbon with fewer hydrogen.
The Role of the Solvent in S N 1 S N 2 E1 and E2 Reactions. Drawing alkyne formulas from names. The S N 2 doesnt happen for secondary alcohols.
A recent application is the generation of highly reactive aryl radicals which are useful arylating reagents in synthesis by photoinduced electron transfer PET from photoredox catalysts to suitable precursors followed by bond scission 8 9However the choice of aryl radical precursors is currently limited to electron-poor arenes such as diazonium 6 10 or. Drawing formulas from names. In addition to primary amines secondary amines led to reductive coupling with nitriles and provided tertiary chiral amines in up to 85 yields and 99 ee Fig.
From alkenes i By acid catalysed hydration. Dehydration can be performed in a 3-step mechanism. Formation of protonated alcohol.
Mechanism of Dehydration of Alcohols. In case of unsymmetrical alkenes the addition reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikovs rule Unit 13 Class XI. For instance alkanes alkynes or alkenes the amount of bonded hydrogen decreases in alkenes and alkynes.
Markovnikovs Rule with Practice Problems. Drawing alkene formulas from names. The elements of water can be added to the doublebonded carbons of an alkene in either a Markovnikovs or an antiMarkovnikovs manner.
Theres no warning sign saying wait. Dehydration of alcohols follows the E1 or E2 mechanism. Represented by R-Mg-X where R is an alkyl or aryl group while X is a halogen the Grignard reagent easily forms a carbon-carbon.
In four textbooks where SOCl 2 is mentioned the reaction is shown as proceeding through an S N 2 mechanism.

Electrophilic Addition Reactions Of Alkenes Mcc Organic Chemistry
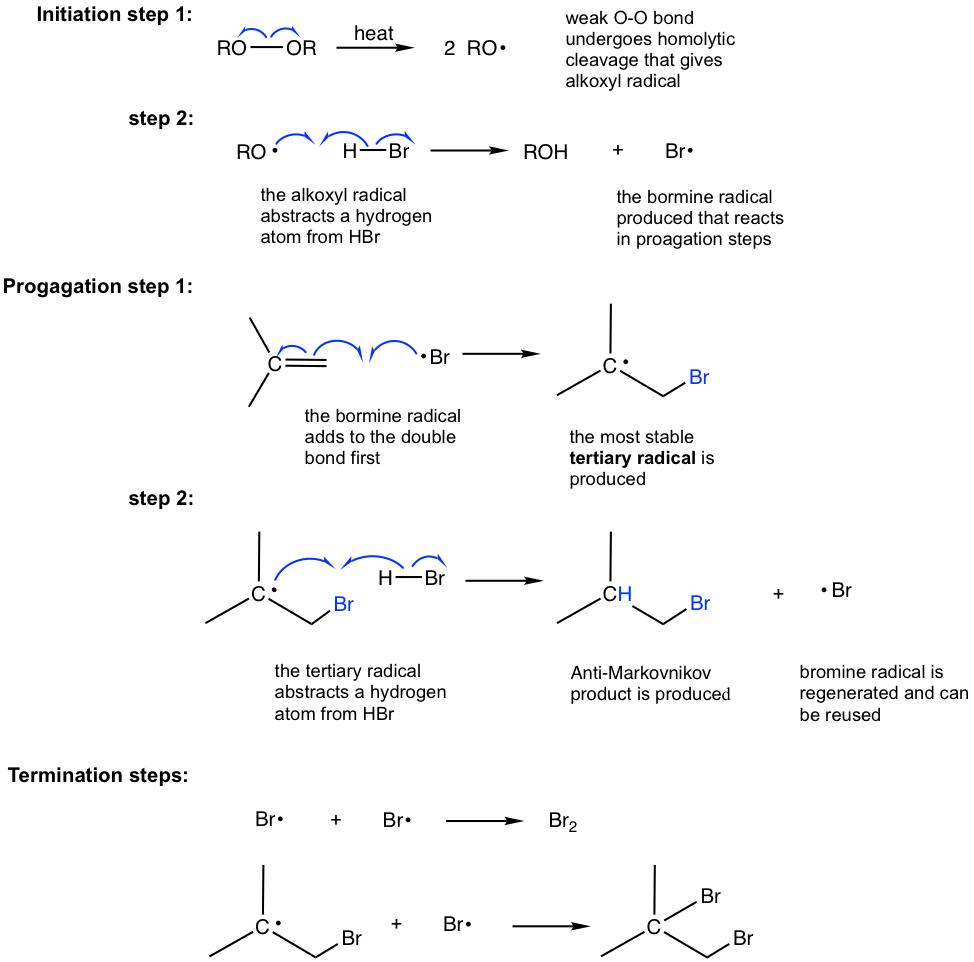
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
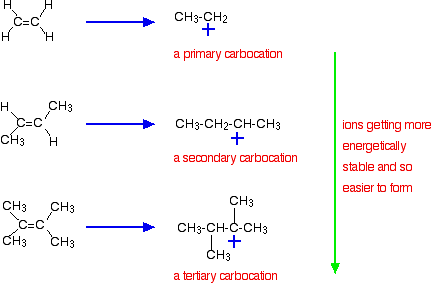
9 2 Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Symmetrical Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts

Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment